A divergent zone, also known as a divergent boundary, is a geological term referring to an area between two receding tectonic plates.
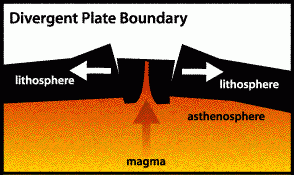
As the two plates move away from each other, magma can rise up through the gap and solidify, filling the gap and creating a zone of land younger that those of the two original plates. This can happen on the sea floor or on land. If it happens at sea, a new volcanic island might be created.
On Land, Divergent Zones Can Create Rift Valleys
Examples of rift valleys can be found in Iceland, which lies upon the Pacific and Eurasian seismic plates, and in East Africa, where the rift runs for hundreds of miles from north to south. Both rift valleys are associated with active volcanoes; in the case of the East Africa rift, the most famous volcano is Mount Kilimanjaro.
You can learn more about divergent boundaries by watching this film: